All humans are different. In fact, some people aren’t even human… Some people are French, and that is tragic. But being French is not the only known genetic mutation. As it turns out, it’s not even the strangest. Here are some of the rarest and most incredible human genetic mutations in existence.
Rare Genetic Mutations
Super Strong Bones
Some people have unbreakable bones – or at least, almost unbreakable. Bone density is regulated by the lrp5 Gene – and a mutation in said gene can either cause your bones to be less dense, and therefore weaker than average – or more dense to the point of being ridiculous. It took decades for scientists to find the gene. Then in the late 90s they found a single family in the state of Connecticut, who have extremely dense bones, and usually an especially large lower jaw bone.
20 members of that family donated blood to science. And while this did not reveal them to be aliens from a distant planet, it did show they had an LRP5 Gene mutation. The mutation simple caused the gene to be more effective, assigning more calcium to bone growth. Still today, research is being done into how the mutation could be genetically engineered – so maybe all future children will have unbreakable bones.
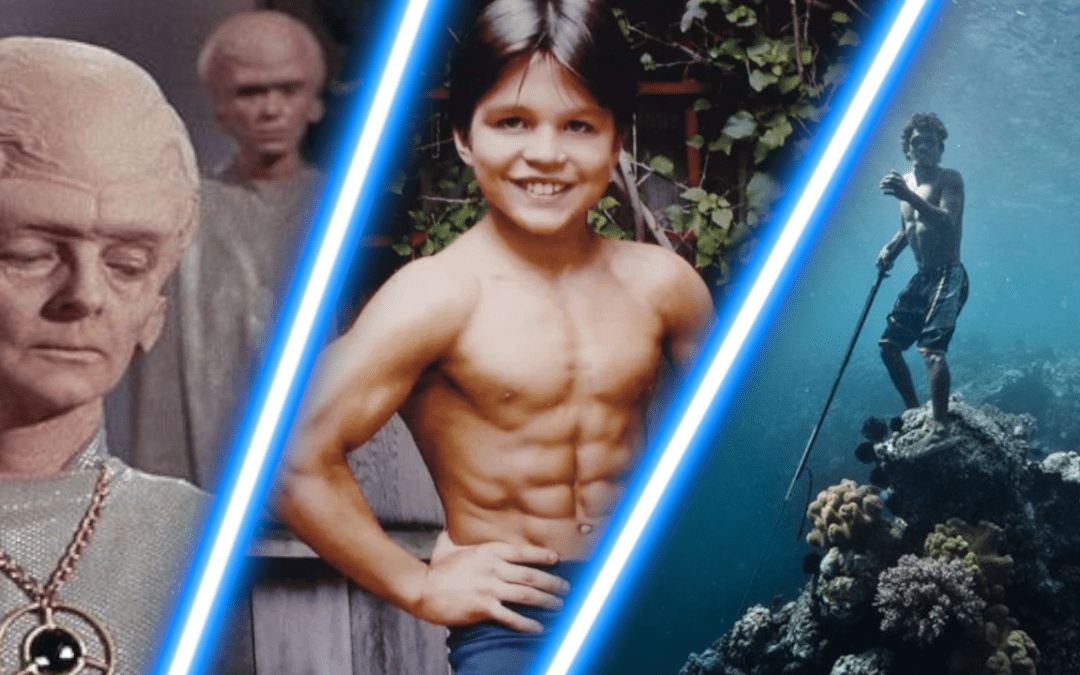
Super Strength
They might also have super strength, as there is another mutation that causes crazy muscle growth. Even without regular exercise, people with the mutation are naturally jacked – including children. Yes, they look like they’ve been raised on a diet of steroids and creatine. And yes, they probably punch dry wall, but it’s entirely natural.
This particular mutation is associated with Myostatin, a protein responsible for regulating tissue growth. In other words, it limits the amount of muscle your body can naturally produce. But in some incredibly rare cases, people are born with an inhibited Myostatin production. So with less guardrails, their body simply builds bigger and stronger muscles. Quite often, people with the mutation have double the muscle mass of an average human, even without lifting weights.
They also have lower than average body fat. Best of all, there are no known negative health issues associated with the condition. So it’s basically just a cheat code. It is known as muscular hypertrophy, and is evident from birth. But it’s not only present in humans. Cattle are especially prone, with 7 known genetic mutations causing low myostatin production. And the thing is, cows are already pretty strong, so these guys look ready to be sent into battle.
As you’d expect, scientists have long been developing gene editing techniques to inhibit myostatin. In fact, in one experiment, mice were induced to have four times the muscle mass they otherwise would have.
Super Pain Tolerance
Believe it or not, some people are unable to feel pain. I’m speaking specifically about physical pain, of course. Even they can’t avoid the pain of embarrassment… Like that time I saw a man get headbutted by a horse. That was embarrassing. Known as Congenital insensitivity to pain, or CIP, it is incredibly rare, and caused by mutations in the SCN9A gene – which regulates nerve impulses. In short, it prevents your brain from signalling when things go wrong – and the way our brain does that is through physical pain.
So while a painless life might sound great, it’s actually a huge disadvantage. If you go through life totally unaware of when things are going wrong in your body, bad things will happen.The mutation is a curse, with minor health issues going unnoticed, often until far too late. As you can imagine, it’s hard for affected children to learn what is unsafe, given their total indifference to getting burnt or cut open. As a result, many with CIP die during childhood. Currently, there are 3 known genes which can cause the disorder, and in one experiment, Mice were successfully given CIP. Just like in humans, the mice experienced no fear in the face of extreme heat and cold.
As a result, treatments were discovered to relieve the symptoms of CIP, literally granting affected adults the ability to feel pain – which if we’re being honest, has got to suck after a lifetime of numbness.
The Bajau people
In South East Asia there is a totally unique tribe of people. They are the Bajau, and for thousands of years they have lived at sea. For food they dive, and hunt deep underwater – and some spend more than half of their day below the surface. As a result, they have adapted, evolved to be real life fish people… And when I say real life fish people, I just mean they can hold their breath pretty long.
Having a bigger spleen than other humans, the Bajau can make better use of oxygen while holding their breath, enabling them to stay underwater 3 or 4 times as long as we can. They spend very little time on land, preferring either boats or floating platforms – to the point they stateless. No country in south east Asia claims them as citizens. Instead, they drift wherever the ocean takes them. But the main point is, they are fish people.
Polydactyly
One of the more visible genetic mutations is Polydactyly, a ridiculous name for an only semi ridiculous condition. It’s actually the most common hand and foot defect, and simply means you have an extra finger or toe. Some even have more than one extra. For many, it is tiny nub without any bones, and only a hindrance to hand function – but in others, it can be a fully movable finger or toe. The exact causes of Polydactyly are unknown, but mutations in 39 genes are associated with the condition – one of which is literally called the Sonic Hedgehog Gene… So that’s weird.
It affects only around 1 in a thousand people. Which now that I think about it is actually quite a lot. But most get their extra digits surgically removed while still a child. Many species of animal can have Polydactyly, from horses to chickens. But it seems most common in cats. Similar mutations cause related conditions, such as Ectrodactyly, where the hands or feet are typically split apart. It’s a result of missing bones, causing the flesh to form into a claw like shape. Luckily, Ectrodactyly is much more rare, typically affecting 1 in 90 thousand people.
Super Sleep
Other mutations include super flexibility, photographic memory, and the ability to see shades of colors no one else can. But the one I’m most jealous of is the sleep gene. Most humans need 7 or 8 hours of sleep per night. Get less and you’re body just won’t function optimally. But a mutation in the gene SIK3-N783Y cuts that requirement in half. People with it not only get by with just 4 hours sleep, they thrive on it. It’s thought they simply sleep more efficiently than we do – and when the gene mutation was introduced to mice with Alzheimer’s disease, their health noticeably improved. So maybe less sleep is somehow better.