Vestigial body parts are organs that our ancestors had for survival purposes but slowly diminished over time, so that they no longer fulfill a function but haven’t completely gone away. Many vestigial organs go unnoticed and people don’t even know they have them, but some can cause problems and need to be removed. Animals evolve based on their environment, so it’s normal for animals to develop vestigial organs when a function or feature s no longer subject to positive selection pressures in a changing environment.

Your Appendix
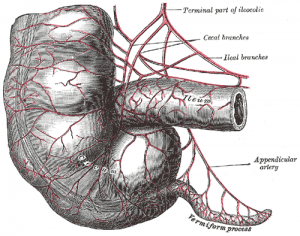
The appendix is believed to be useless by many people all over the world, as thousands of ordinary people have it taken out in appendectomies. The appendix is believed to come from a plant eating ancestor. Your appendix is a small pocket protruding from the large intestine, where it joins the small intestine. Even though it’s attached to the large intestine it doesn’t appear to help digestion in any way. Whether the appendix actually does anything is unknown. Considering so many people have appendectomies and don’t notice any different it’s likely that it either does nothing, or what it does is so minor we don’t really need to care.

Male Nipples
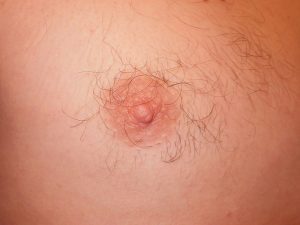
A lot of people have wondered why men have nipples when they serve no real purpose. They may also know that all mammals have nipples and not know why. The reason is because when we are in the early stages of fetal development we are without a sex. The sex of a foetus is decided later on with the release of testosterone. If a foetus has the y chromosome then testosterone will be released to make it a male, if there isn’t a y chromosome then it will be female. Male nipples are essentially functionless, making them vestigial although they can be dangerous to humans, as they can develop forms of cancer.

Wisdom teeth
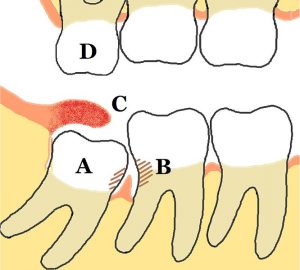
Wisdom teeth can be some of the most painful vestigial body parts in humans. Wisdom teeth appear and try to force their way into a mouth that doesn’t have any room for them. They force their way into an already full mouth causing a a lot of pain, blood and discomfort. Normally people will hire a professional to take them out when the pain becomes too much. The reason these teeth became vestigial could be a variety of things. It may be that our ancestors had bigger jaws, and as ours became smaller we simply ran out of room for wisdom teeth. It could be because we brush our teeth now. In the past our ancestors wouldn’t brush their teeth, some of their teeth would fall out and the wisdom teeth would be a good back up.

The Coccyx
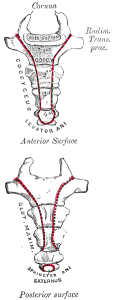
The Coccyx is a part of your vertebrae. It’s commonly known as the tail bone because it is actually the last remaining part of the tail we once had. Humans used to have tails for balance, but as we began to stand up straight we no longer needed it and it slowly disappeared. The remaining coccyx is now vestigial. Some people have had there’s taken out and it hasn’t seemed to have affected the. Although humans generally don’t have tails there have been some humans born with tails. In fact all humans have tails tails while they are still developing in the womb, it can even be observed a lot of the time.

Arrector Pili
Arrector Pili are the muscle fibres that cause goose bumps to appear when you’re cold or nervous. This helps animals with a lot fur because it helps them trap a lot heat between erect hair follicles. This can help animals stay warm in cold environments, but it can also make animals appear bigger than they actually which can scare off predators, by making them look like tougher prey. Although to some animals it may just look like a bigger meal. This doesn’t apply for humans as we don’t have any fur, and our body hair is pretty minimal goosebumps fail to keep us warm, or make us look any bigger than we actually are.

Third Eyelid
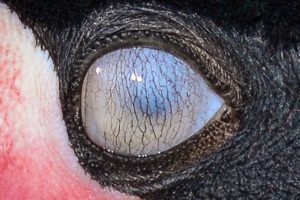
Copyright Olaf Oliviero Riemer / (CC BY-SA 3.0)
The Nicitating membrane is a translucent third eye lid that humans used to have. It would blink from side to side and was meant to protect the eye without inhibiting visibility. You can see this in cats if you look closely, as they blink you’ll see a third eyelid. We still have a vestigial remnant of this in our eyes which can also be seen if you look closely. It’s easier to see in Australians and Africans. At some point we must have needed a third eyelid to survive, but eventually the need fro it disappeared and we didn’t need to use it any more, and it eventually disappeared.

Palmar Grasp Reflex

You’ve probably seen this either in real life or in a film, but when a baby is very young, it will actually squeeze your finger if you put it in it’s hand. This is reflex that normally lasts for the first six months after a baby is born. In the past humans were covered in body hair and a baby would use this vestigial reflex to grab onto it’s mothers coat. This was especially useful when trying to escape predators. The mother could carry the baby while running away with both her hands, and feet free.
 Darwin’s tubercle
Darwin’s tubercle

Copyright André Ueberbach / (CC BY-SA 2.0 DE)
Although Darwin’s tubercle can be found n the majority of mammals, it”s unusual for humans to have them. In fact only about 10% of humans have it at all. It’s purpose was probably to focus sounds in animals. In humans it doesn’t serve that function, and doesn’t to do anything for us at all. Even though most of us have don’t have the vestigial point a lot of people may have the gene anyway, since having the gene doesn’t guarantee the point will appear. The point is a small protrusion in the upper middle part of the ear, it can appear in other places in different animals.

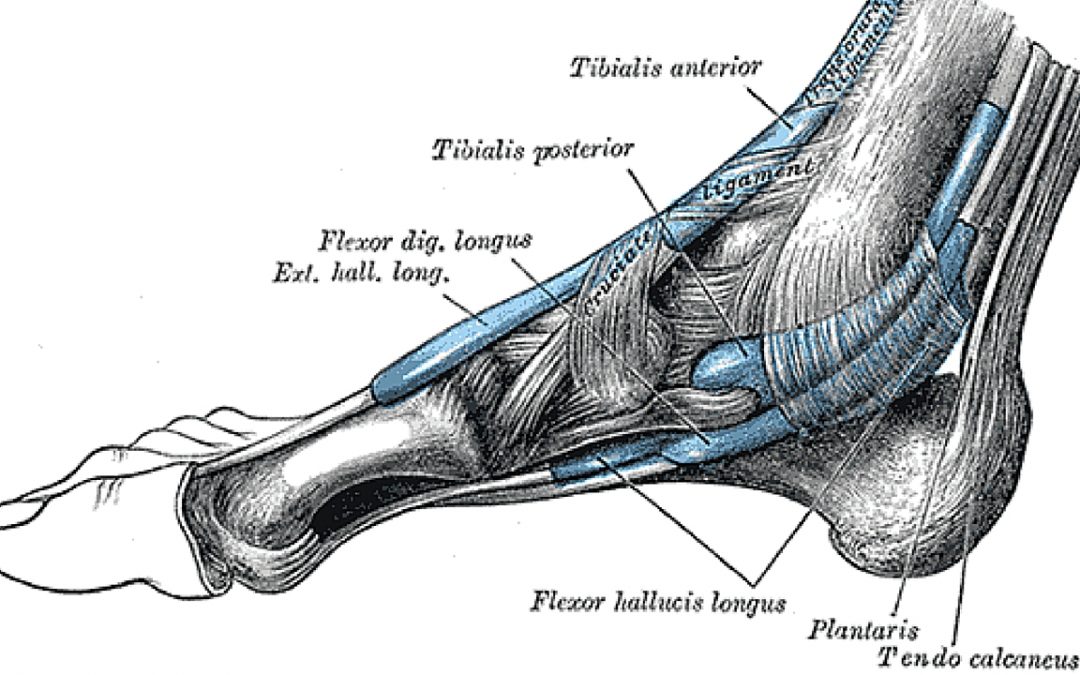
The Plantaris Muscle
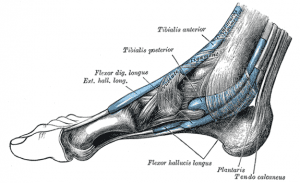
The plantaris muscle is a muscle in the foot that allows animals to pick up and manipulate objects with our feet. This is how apes are able to eat and pick things up with their feet. Most humans have the muscle but don’t use it so it becomes weak, and can’t really be used. This is because most of us get through our lives without having to use our feet to pick things up. Although there are some people who train to be able to manipulate objects with their feet. This vestigial muscle has become so underused that 9% of people aren’t even born with it any more.

Sinuses
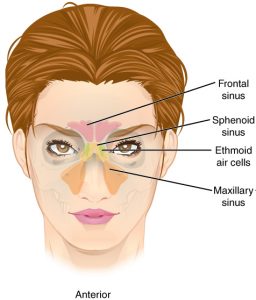
Copyright CFCF / (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Sinuses are air pockets in your face, and nobody really knows what they do. As well as air, bacteria can also get inside these pockets leading to painful, infections, and sinus headaches. Like most vestigial body parts, no can agree what it actually but there are a lot theories. Our ancestors may have been given a stronger sense of smell because of sinuses. Sinus infections can cause a lot of pain, as well as sinus discharge, headaches, and coughs, and all from something you don’t even need.
Our Video On This: